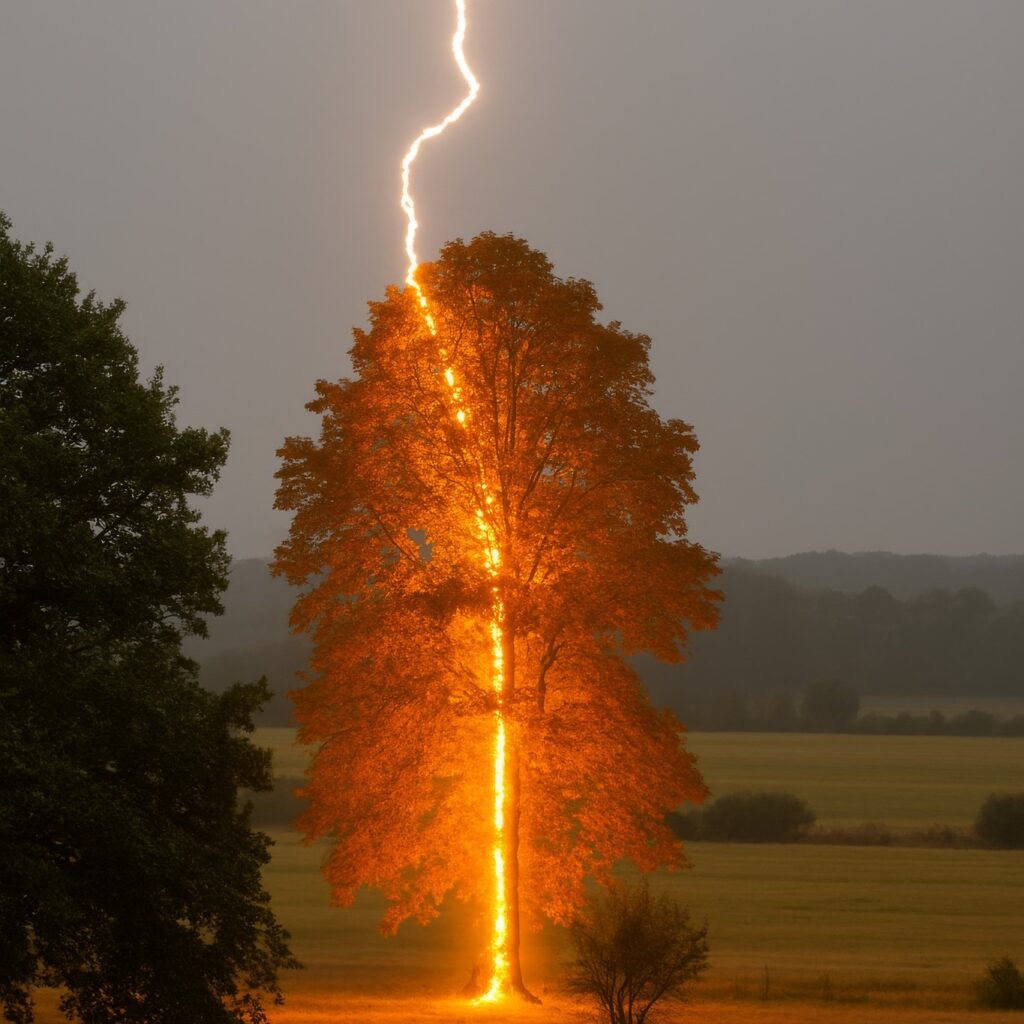

Lightning protection is essential for safeguarding structures, equipment, and lives from the destructive force of lightning strikes. Various methods are employed to mitigate the risks associated with lightning by directing its high voltage energy safely into the ground.
One of the most common and effective methods is the lightning rod system. Invented by Benjamin Franklin, a lightning rod is a pointed metal rod installed on the highest point of a structure. It is connected via conductive cables to a grounding system. When lightning strikes, the rod intercepts the discharge and channels it into the earth, preventing damage to the building.
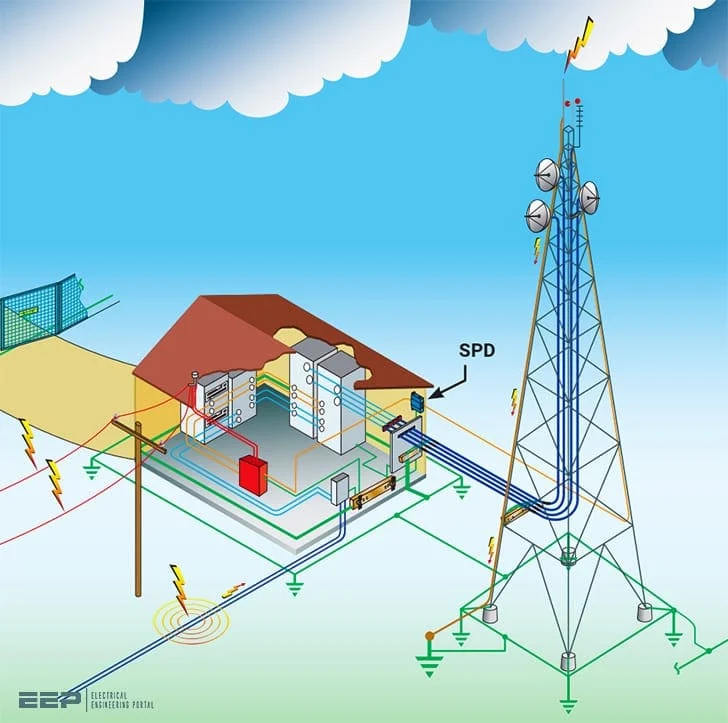
Surge protection devices (SPDs) are another important method. These devices are installed in electrical systems to protect sensitive electronics and wiring from voltage spikes caused by lightning. SPDs work by diverting excess voltage to the ground, thereby safeguarding appliances and systems like computers, HVAC units, and telecommunications equipment.
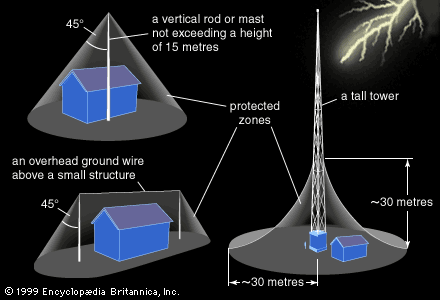
Grounding systems are vital for any lightning protection plan. A proper grounding system consists of conductive materials, such as copper or galvanized steel, buried in the earth. These materials provide a low-resistance path for lightning to safely dissipate its energy. The effectiveness of grounding depends on soil composition and moisture levels, making proper installation crucial.
In areas with frequent thunderstorms, early streamer emission (ESE) systems or charge dissipation terminals may be used. These advanced technologies are designed to attract or prevent lightning strikes more effectively over large areas, such as industrial facilities or tall structures.
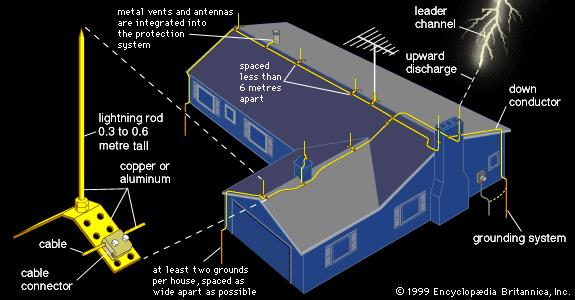
Overall, a comprehensive lightning protection system combines structural protection, surge protection, and effective grounding. Regular maintenance and inspections ensure continued performance and safety. As climate change increases the frequency of severe weather, implementing reliable lightning protection methods becomes increasingly important for protecting property and human life.



